How does the government use GPS?
All vehicle location data is transmitted wirelessly by either cellular or satellite communication. Government fleets use fleet tracking technology to monitor fuel usage, improve routing, control labor costs, improve public and driver safety, and so much more gained from location intelligence.
Who uses GPS and how is GPS used?
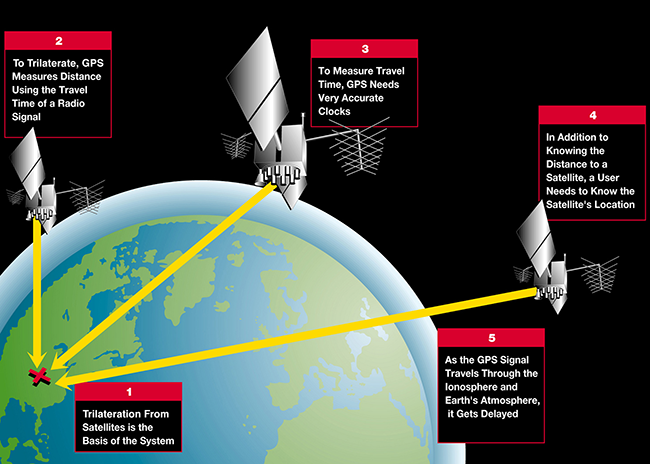
This method of determining location is called trilateration. Aircraft, ships, submarines, trains, and the space shuttle all use GPS to navigate. Many people use receivers when driving cars.
How does GPS benefit society?
For example, GPS can be used for everything from finding your way around a new city to tracking commercial shipping containers as they travel around the globe. In addition, GPS provides critical data for weather forecasting, agricultural planning, and even disaster relief efforts.
Who benefits from GPS?
Installing GPS tracking in your cars and various assets ensures that your business can track its location. It also enables you to identify any strategy and behavior with the drivers. The authorities recover your assets, thus lowering insurance and replacement costs by monitoring your vehicles\' location.
Why is GPS important?
The Global Positioning System (GPS) has changed the way the world operates. This is especially true for marine operations, including search and rescue. GPS provides the fastest and most accurate method for mariners to navigate, measure speed, and determine location.
How does the military use GPS?
Like the bulk of so many commercial industries, U.S. military forces depend heavily on GPS. For the military, GPS enables navigation in hostile territory; precise munitions guidance; location of casualties; and fusing of data for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR).
How important is GPS in the economy?
What are 15 uses of a GPS?
Perhaps the most common use for GPS is in navigation systems. Combined with map technology, it becomes a powerful tool for road vehicles and boats. GPS can pinpoint a device's location with accuracy and by comparing coordinates, the statistics can be used to calculate a device's direction of movement and speed.
How does GPS make money?
GPs are independent contractors working for the NHS, and do not receive a salary. Each practice has individual funding, calculated through a complex process of national guidelines and local negotiations. The surgery receives funding for the day-to-day running of the practice, and pays the doctors and staff from this.
How does GPS get money?
Who Pays for GPS? The American taxpayer pays for the GPS service enjoyed throughout the world. All GPS program funding comes from general U.S. tax revenues.
What is the most common use for GPS?
1. Locating Positions. This is the main and most common application of GPS—tracking locations.
How many people use GPS?
It is essential to vehicle navigation systems, general aviation, financial transactions, the electrical grid, precision agriculture, surveying, and construction. Americans use over 900 million GPS receivers.
Who are the main users of GPS?
GPS is used by aircraft and ships for enroute navigation and for airport or harbor approaches. GPS tracking systems are used to route and monitor delivery vans and emergency vehicles.
Who operates the GPS system?
Currently 31 GPS satellites orbit the Earth at an altitude of approximately 11,000 miles providing users with accurate information on position, velocity, and time anywhere in the world and in all weather conditions. GPS is operated and maintained by the Department of Defense (DoD).
When was the GPS used?
The United States Department of Defense started the GPS project in 1973. The first prototype, called the Block-I GPS satellite, was launched in 1978 from Vandenberg Air Force Base. In 1990 and 1991, the U.S. military relied heavily on GPS during the Gulf War with Operations Desert Shield and Desert Storm.
Which country uses GPS?
There are four core satellite navigation systems, currently GPS (United States), GLONASS (Russian Federation), Beidou (China) and Galileo (European Union). Global Satellite-Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) such as OmniSTAR and StarFire.
Who controls the GPS system?
Currently 31 GPS satellites orbit the Earth at an altitude of approximately 11,000 miles providing users with accurate information on position, velocity, and time anywhere in the world and in all weather conditions. GPS is operated and maintained by the Department of Defense (DoD).
Why does the military need GPS?
More precisely, the military is critically dependent on the GPS satellite system due to its ability to provide three-dimensional positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) information for countless military systems.
Why is GPS important in aviation?
Aircraft must normally fly from point to point to navigate to their destination. Flight paths are rarely direct. With the advent of GPS, exact positional information is available to pilots. This enables direct routes, reduced flight times and reduced fuel consumption.
Why is GPS reliable?
With the distance information collected from multiple ground stations, the location coordinates of any satellite at any time can be calculated with great precision. Each GPS satellite carries an accurate record of its own position and time, and broadcasts that data continuously.
How does GPS affect the environment?
GPS receivers are also embedded in many bulldozers, excavators and graders, resulting in reduced waste and lower fuel consumption. They can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, with an estimate from Trimble suggesting that the use of machine control technologies can cut more than one billion pounds of CO2 usage per year.
Why is GPS important in transportation?
GPS tracking technology has become the most popular choice for making transportation businesses highly productive. GPS allows you to track the location of your vehicles, find out the time and thus the cost per delivery, and allow you to optimise deliveries based on daily and weekly patterns that you see in traffic.
What are the pros and cons of GPS?
GPS technology offers a wide range of benefits, such as increased efficiency and productivity, enhanced safety, improved accuracy and precision, and cost-effectiveness, but it also has its disadvantages, such as dependence on satellites, privacy concerns, cost, and reliance on technology.
What data does GPS use?
To determine the location of the GPS satellites two types of data are required by the GPS receiver: the almanac and the ephemeris. This data is continuously transmitted by the GPS satellites and your GPS receiver collects and stores this data.
Who owns GPS data?
Today, GPS is a multi-use, space-based radionavigation system owned by the US Government and operated by the United States Air Force to meet national defense, homeland security, civil, commercial, and scientific needs.